Product Consultation
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
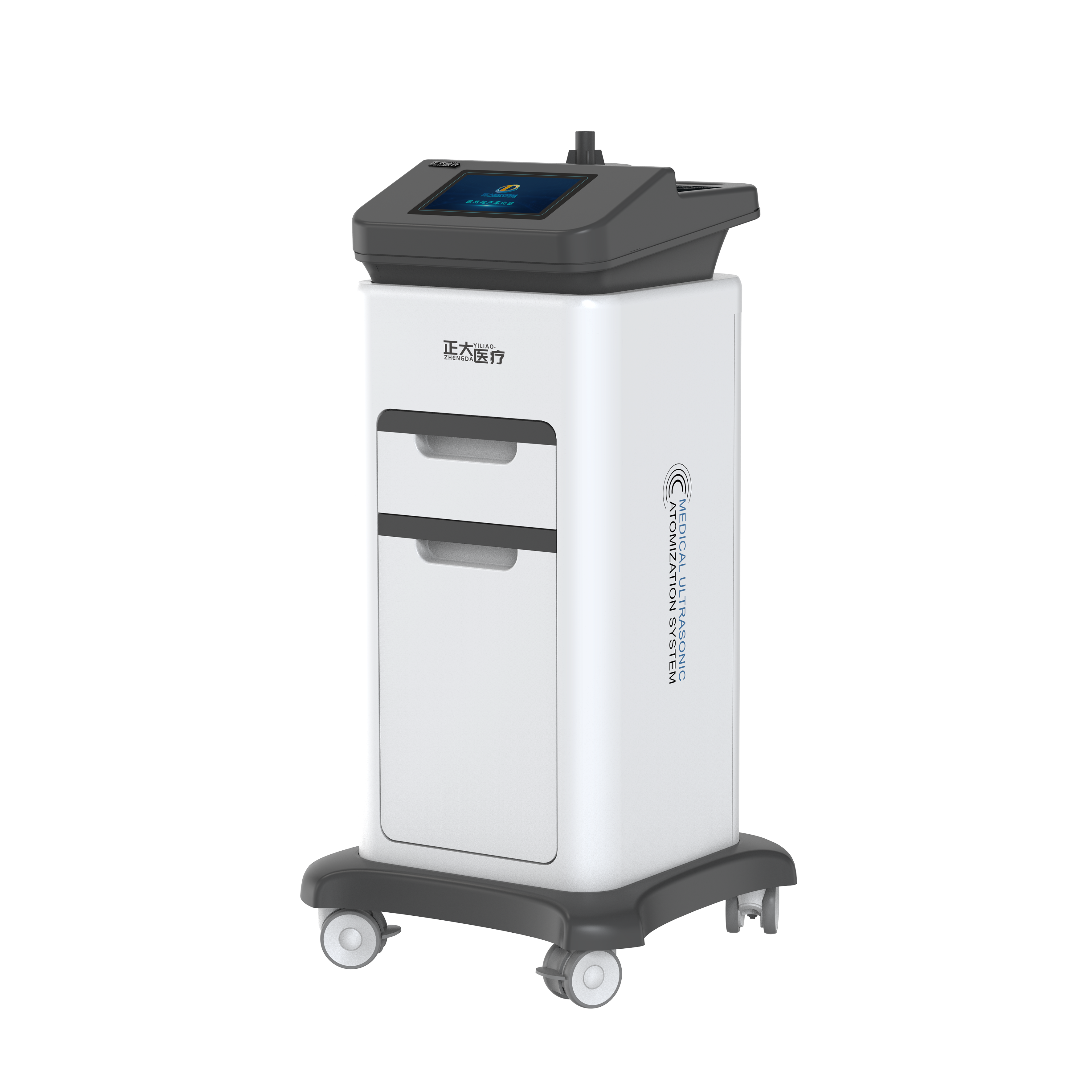


In the field of modern medicine, medical ultrasonic atomization systems are a common way of drug administration. With its advantages of simple operation, high drug utilization rate and good patient comfort, they are widely used in the treatment of respiratory diseases. The system converts water or liquid medicine into tiny particles through ultrasonic vibration, making it easier for patients to inhale the medicine and directly reach the lesion, thereby accelerating the remission of the disease. However, any medical technology has its limitations, and the medical ultrasonic atomization system is no exception. This article will explore in depth the limitations of the medical ultrasonic atomization system in terms of the non-selectivity of atomized particles, the possible excessive humidification of the respiratory tract and the risk of hypoxia, and propose personalized application strategies based on the specific conditions and conditions of the patients.
Non-selectivity of atomized particles: affecting the treatment effect
A notable feature of the medical ultrasonic atomization system is that its atomization process lacks precise control over the particle size, which means that the drug particles produced are of different sizes, most of which are larger in size and mainly deposited in the upper respiratory tract areas such as the mouth and throat. For diseases that require deep lung (i.e. lower respiratory tract) treatment, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and bronchial asthma, this non-selective atomization effect may make it difficult for drugs to effectively reach the target area, thus affecting the treatment effect. In addition, the deposition of large-particle drugs in the mouth and throat may also cause local irritation and increase the patient's discomfort.
Excessive humidification of the respiratory tract and the risk of hypoxia
During the ultrasonic atomization process, due to the large size of the mist particles and the fast atomization speed, patients often inhale a large amount of water vapor. Moderate respiratory tract humidification helps dilute and discharge sputum, but excessive humidification may be counterproductive. Excessive water vapor will increase the moisture content in the respiratory tract, resulting in increased respiratory resistance and poor breathing. For patients who already have narrow or impaired respiratory tract function, this increased resistance may further limit oxygen exchange and induce or aggravate hypoxia, especially during rapid atomization, when patients inhale a large amount of mist in a short period of time, and the risk of hypoxia is particularly prominent.
Personalized application strategy: the key to precision treatment
Given the above limitations, the effective application of medical ultrasonic atomization systems is highly dependent on the specific conditions and conditions of patients. The following strategies can help achieve more accurate and safe treatment:
Condition assessment and individualized plan: Before use, the doctor should evaluate the patient's respiratory condition, disease type and severity in detail, and formulate a personalized nebulization treatment plan based on this, including selecting appropriate drugs and adjusting nebulization parameters (such as nebulization time, frequency, drug concentration), etc.
Monitoring and adjustment: During the treatment, closely monitor the patient's response, including indicators such as respiratory rate and blood oxygen saturation. Once increased respiratory resistance and signs of hypoxia are found, nebulization should be stopped immediately and appropriate emergency measures should be taken.
Combination of auxiliary means: For lower respiratory tract diseases, other drug administration methods can be considered, such as using a compressed air nebulizer with smaller particles, or combining physical therapies such as postural drainage and back patting to increase the deposition rate of drugs in the lower respiratory tract.
Patient education and guidance: Strengthen health education for patients so that they understand the purpose, method, possible adverse reactions and countermeasures of nebulization treatment, improve self-management ability, and reduce discomfort and risks during treatment.

Plaster saw blade service life and maintenance strategy: the key to ensuring efficiency and safety
Nov 14,2024
Hangzhou Zhengda Medical Moxibustion Therapy Device Helps Health Management
Jul 24,2025Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Spine Operating Support

Medical Ultrasonic Atomization System

Expectoration Therapy Instrument Series

Magnetic therapy products
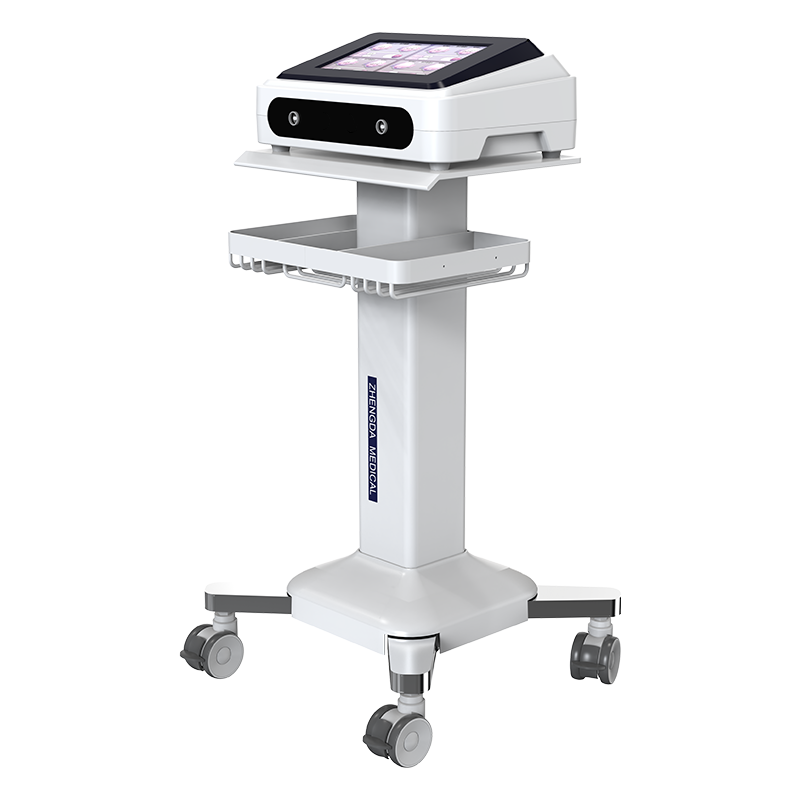
Electrotherapy series products
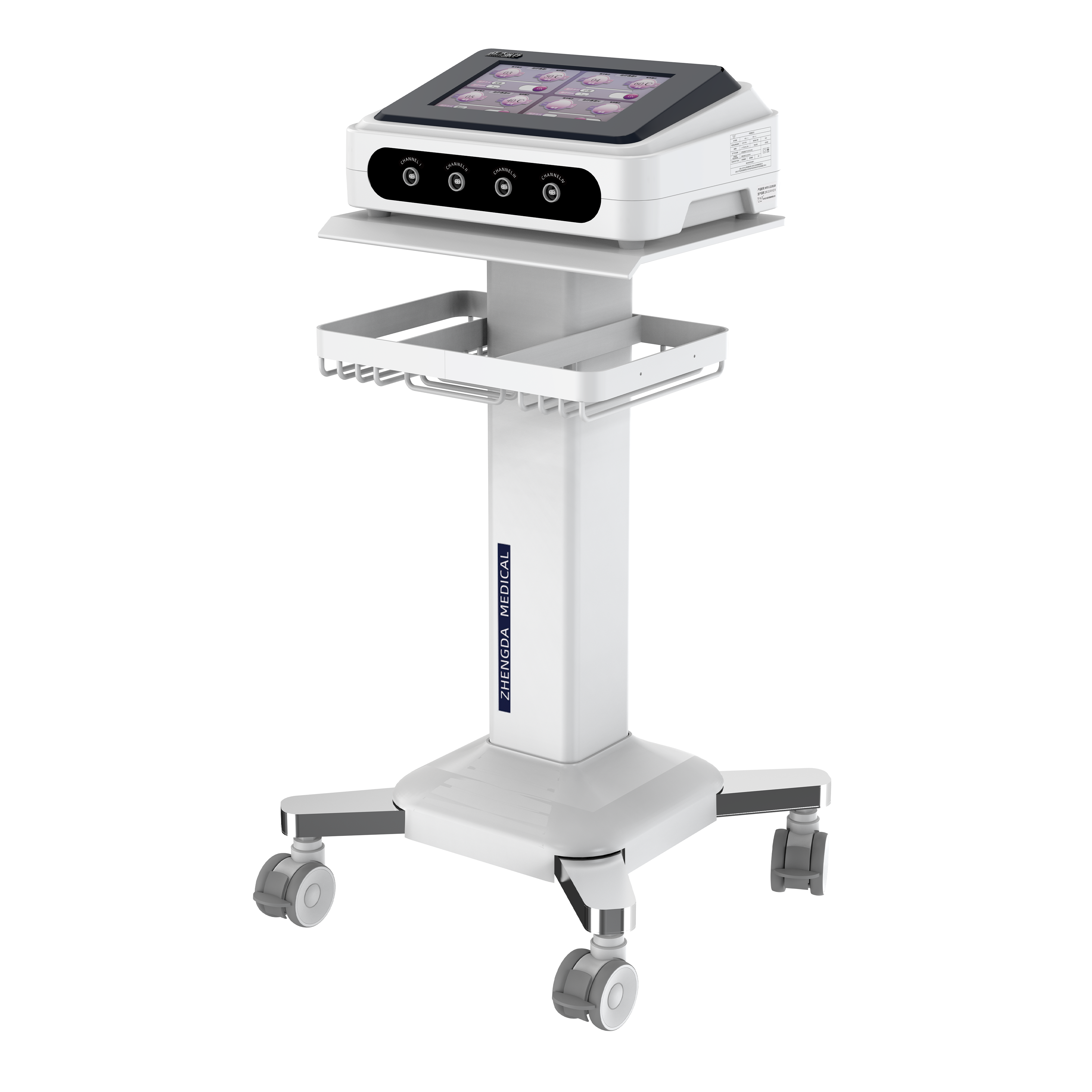
Electrotherapy series products

Cervical and Lumbar Traction System
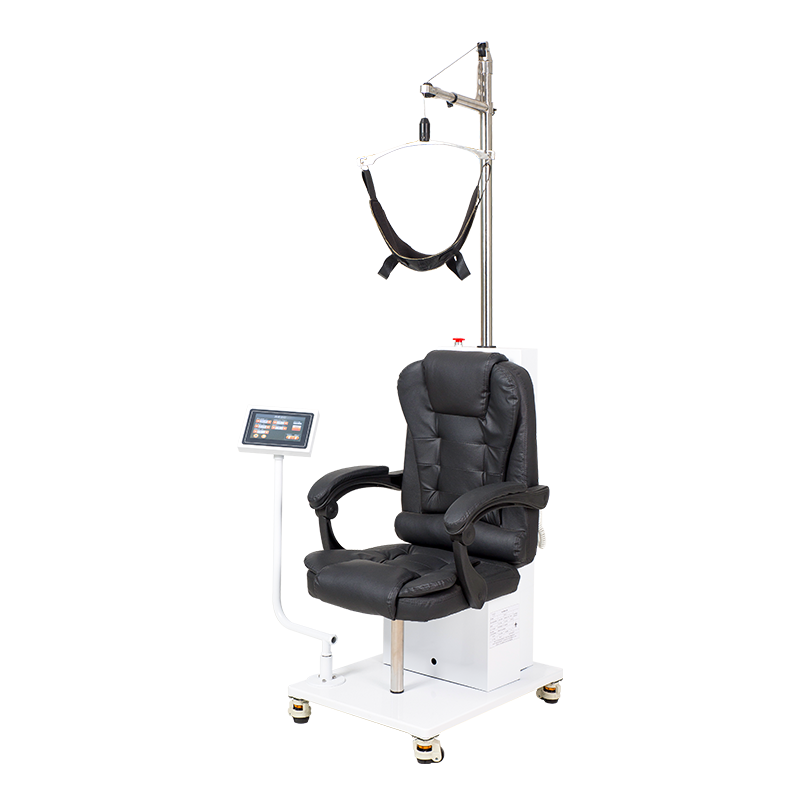
Cervical and Lumbar Traction System

Pneumatic Finger Trainer

Massage System

Orthopaedic power tools

Compression Therapy System

COPYRIGHT © Hangzhou Zhengda Medical Equipment Co.,Ltd ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
Custom medical equipment Manufacturers
The information provided on this website is intended for use only in countries and jurisdictions outside of the People's Republic of China.